Posizioni tra due piani
Fissato un rif. cart. ortonormale \(RC(O, i,j,k)\) si dispongono delle equazioni cartesiane di due piani.
\(\alpha = ax+by+cz+d=0\)
\(\beta = a'x+b'y+c'z+d'=0\)
Lo studio della reciproca posizione si basa sul calcolo del rango delle matrici incompleta \(A\) e completa \(A|b\) associate al sistema lineare formato dalle due equazioni. In altre parole corrisponde allo studio della compatibilità del sistema. Rouché Capelli:
- se \(rk(A) =2\) allora \(rk(A|b)=2\) e quindi il sistema ammette \(\infty^1\) soluzioni. I piani sono incidenti, e le soluzioni sono tutti e soli i punti della retta lungo cui i due piani si intersecano. La direzione della retta è data dal prodotto vettoriale dei coefficienti direttori dei piani: \({\textbf v} = (a,b,c) \times (a',b',c')\). Se il prodotto scalare è nullo (\((a,b,c,) \cdot (a',b',c')=0\)) i vettori sono ortogonali, dunque i piani sono incidenti e perpendicolari.
- se \(rk(A) = 1\) ci sono due casi:
- se \(rk(A|b)=2\) allora il sistema è incompatibile, quindi i piani sono paralleli distinti.
- se \(rk(A|b)=1\) il sistema ammette \(\infty^2\) soluzioni, dunque i piani sono paralleli coincidenti.
Questa sezione chiarisce molto bene la rappresentazione gemetrica e spaziale dei sistemi lineari, e il significato delle soluzioni ammesse.
Funzione riassumibile
import sympy as sp
from typing import List
from ipynb.fs.full.piano_equazioni_parametriche_equazione_cartesiana import equazioniParametrichePianoToEquazioneCartesiana
def posizioneTraPiani(alpha_parametriche: List[sp.Matrix] = None, beta_parametriche: List[sp.Matrix] = None, alpha_cartesiana: sp.Matrix = None, beta_cartesiana: sp.Matrix = None) -> sp.Matrix:
"""
Restituisce:
- PARALLELI_DISTINTI (str)
- PARALLELI_COINCIDENTI (str)
- Retta di intersezione (sp.Matrix)
"""
s,t,x,y,z = sp.symbols("s t x y z")
if alpha_parametriche is not None:
alpha_cartesiana = equazioniParametrichePianoToEquazioneCartesiana(alpha_parametriche, s, t)
if beta_parametriche is not None:
beta_cartesiana = equazioniParametrichePianoToEquazioneCartesiana(beta_parametriche, s, t)
A, b = sp.linear_eq_to_matrix([alpha_cartesiana, beta_cartesiana], sp.symbols("x y z"))
Ab = sp.Matrix([[A, b]])
rangoA = A.rank()
rangoAb = Ab.rank()
if rangoA is 2:
a_coeffs = alpha_cartesiana.as_coefficients_dict()
b_coeffs = beta_cartesiana.as_coefficients_dict()
v = sp.Matrix([[a_coeffs.get(x) if a_coeffs.get(x) else 0, a_coeffs.get(y) if a_coeffs.get(y) else 0, a_coeffs.get(z) if a_coeffs.get(z) else 0]])
v1 = sp.Matrix([[b_coeffs.get(x) if b_coeffs.get(x) else 0, b_coeffs.get(y) if b_coeffs.get(y) else 0, b_coeffs.get(z) if b_coeffs.get(z) else 0]])
return v.cross(v1)
if rangoA is 1 and rangoAb is 2:
return "PARALLELI_DISTINTI"
elif rangoA is 1 and rangoAb is 1:
return "PARALLELI_COINCIDENTI"
Esempi
x,y,z,h = sp.symbols("x y z h")
h=4
alpha = 2*x + h*y - 2*z + 3
beta = x + 2*y - z - 1
posizioneTraPiani(alpha_cartesiana=alpha, beta_cartesiana=beta)'PARALLELI_DISTINTI'from ipynb.fs.full.common_functions import plotPlanes
h=2
alpha = 2*x + h*y - 2*z + 3
beta = x + 2*y - z - 1
int = posizioneTraPiani(alpha_cartesiana=alpha, beta_cartesiana=beta)
print(int)
# TODO: cambiare spazi dell'area 3d
plotPlanes(equazione_a=alpha, equazione_b=beta, x_space=-5, y_space=5)Matrix([[2, 0, 2]])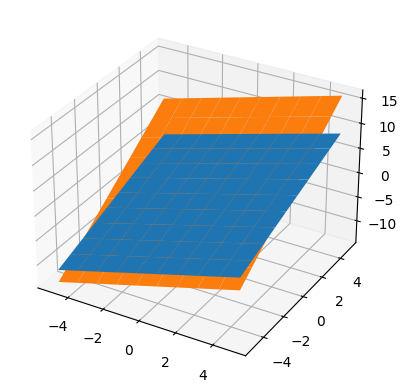
s,t = sp.symbols("s t")
alpha = [
x -1 - s - 3*t,
y - s - t,
z -t
]
beta = [
x - 2*s - 3*t,
y - 1 - t,
z - s
]
posizioneTraPiani(alpha_parametriche=alpha, beta_parametriche=beta)\(\displaystyle \left[\begin{matrix}-1 & 0 & - \frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right]\)
Riferimenti
- https://www.youmath.it/lezioni/algebra-lineare/geometria-dello-spazio/2645-posizione-tra-due-piani.html